Last updated 24th Apr 2021
Cover photo credit to: https://www.hostafrica.co.za/blog/linux/linux-vs-windows-tco-roi-and-more
This page lists the most common activities that should be done first thing after provisioning/installing OS. Of course, I might missed something or added unnecessary steps, so feel free to adjust as needed.
Many of the activities can be done simultaneously, so the order is preferred but it’s not mandatory.
Do not forget to document machine name, IP settings, and passwords.
Windows
Configure IP address, Gateway, and DNS, then test connectivity.
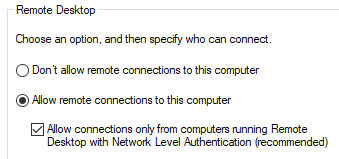
Enable remote desktop if it’s not yet enabled. Make sure to NOT disable NLA.
Install latest updates. I cannot stress enough on this. Additionally, you better enable the options to install updates for other MS products through Windows update, and to notify you when restart is needed.
Select right timezone, and make sure clock is synced. Do NOT set the clock manually. The system should have an NTP to sync with. AD domain member machines are synced with their DC’s, DC’s sync with domain’s PDC emulator, and finally PDC emulator need to be set manually to sync with external source such as (sa.pool.ntp.org) using w32tm command.
Disable services and accounts no more needed such as (cloudbase-init), then create additional administrator account, or reset the password if one already exists like (admin) on STC cloud.
Install Microsoft Edge and, if needed, other browsers.
Install required roles and features.
Install antivirus software if available.
Jump Host
Jump hosts are usually used to access management interfaces of appliances, such as firewalls, load balancers, and others. It can be used as controlled environment to access any other resources or services, such as VPN, SSH, etc. to any system and/or server.
It’s not that common to have jump host running Linux, but it has pretty much the same basics as Windows jump host.
As for Windows jump host, usually it only requires a browser other than IE, and single interface.
In other cases, there might be a need for secondary interface and/or tools, such as VPN or SSH clients.
On Linux, and depending on the targeted systems, an RDP client might needed. Of course in that case the X11 shell must be installed and enabled.
Linux – Debian/Ubuntu
Install latest updates, usually through “sudo apt upgrade” command.
Enable SSH, better to be with certificate authentication and no password login allowed.
Create one more account with password and grant it root access, so login through console would be available in case SSH is broken.
Configure IP address, gateway, DNS, and NTP client.
Linux – CentOS/Redhat
Install latest updates, usually through “sudo yum update” command.
Enable SSH, better to be with certificate authentication and no password login allowed.
Create one more account with password and grant it root access, so login through console would be available in case SSH is broken.
Configure IP address, gateway, DNS, and NTP client.